- Главная
- Предназначение
- Свойства
- Инструкция
- Сертификаты
grade of fuel bren`s

топливо марки bren`s
Increase the service life of engine parts by 30%
Increase the service life of engine parts by 30%
Thanks to its catalytic properties, the Katalgen ® additive brings the process of hydrocarbon oxidation closer to the conditions of an ideal reaction. This tendency leads to a smooth and uniform combustion of fuel, which eliminates the radical, chaotic-explosive nature of heat release. As a result, the thermal load on the parts of the cylinder-piston group is reduced and the service life of the internal combustion engine is increased.
Thanks to its catalytic properties, the Katalgen ® additive brings the process of hydrocarbon oxidation closer to the conditions of an ideal reaction. This tendency leads to a smooth and uniform combustion of fuel, which eliminates the radical, chaotic-explosive nature of heat release. As a result, the thermal load on the parts of the cylinder-piston group is reduced and the service life of the internal combustion engine is increased.
Reducing the thermal load on the plates and valve seats
conventional fuel
fuel with Katalgen® additive


burns out in the exhaust manifold, which creates excessive exposure to high temperatures on the plates and valve seats
completely burns in the engine
cylinders and initiates the oxidation
of previously formed coal deposits
Reducing the thermal load on the plates and valve seats
conventional fuel

burns out in the exhaust manifold, which creates excessive exposure to high temperatures on the plates and valve seats
fuel with Katalgen® additive

completely burns in the engine cylinders and initiates the oxidation of previously formed coal deposits
The pressure force of the expanding gases does not change in magnitude, but its maximum value does not occur at the upper dead center (TDC), but shifts to the middle region of the piston stroke and drops sharply when the piston reaches the NMT. At this point, the fuel burns completely and by the time the exhaust valves are opened, the gas expansion process ends. This is noticeable by reducing the noise level of the engine, since its maximum peak occurs due to a sharp pressure drop at the time of opening the exhaust valves.
The pressure force of the expanding gases does not change in magnitude, but its maximum value does not occur at the upper dead center (TDC), but shifts to the middle region of the piston stroke and drops sharply when the piston reaches the NMT. At this point, the fuel burns completely and by the time the exhaust valves are opened, the gas expansion process ends. This is noticeable by reducing the noise level of the engine, since its maximum peak occurs due to a sharp pressure drop at the time of opening the exhaust valves.
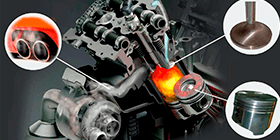
Prevention and cleaning of engine valves, pistons and cylinders
conventional fuel
fuel with Katalgen® additive

consequences of incomplete
combustion of fuel and
octane-cetane additives contained in it
initiates the afterburning of carbon
deposits and
"varnish" coating
When operating an internal combustion engine on petroleum products of various quality, a "varnish" coating is formed on the surface of the combustion chamber from unburned fuel residues and polymers, often included in the composition of octano - or cetano - boosting and depressor additives.
The appearance of a temperature-resistant and oxidation-resistant polymer layer leads to the formation of carbon deposits on the valves, the walls of the pistons and cylinders, the coking of the piston rings and a decrease in the intensity of heat removal through the cylinder walls and the block head from the combustion zone.
Due to overheating and reduced mobility of the piston rings, there is a violation of the cylinder geometry, which leads to a decrease in engine power, to an increase in fuel and engine oil overspending. Once the fuel enters the combustion chamber, the catalysts initiate the oxidation of the inert polymer layer, contribute to its complete burnout and release of the piston rings.
De-coking of the rings increases the compression in the cylinders and returns the regular characteristics of the engine. Further operation of the internal combustion engine on fuel containing the Katalgen® additive eliminates the possibility of destructive processes of formation of deposits in the combustion chamber.
Prevention and cleaning of engine valves, pistons and cylinders
conventional fuel

consequences of incomplete combustion of fuel and octane-cetane additives contained in it
fuel with Katalgen® additive

initiates the afterburning of carbon deposits and "varnish" coating
Prevention and cleaning of intake valves, injectors and fuel system
conventional fuel
fuel with Katalgen® additive


deposits are formed that prevent regular work
initiates the destruction of deposits at the molecular level and contributes to the further prevention of contamination
Modern fuel contains resins, raw water and octane / cetane-boosting additives that contribute to the formation of deposits of oxides and high-molecular compounds upon contact with the surface of the fuel system parts.
The polymer layer, which is inert to dissolution, prevents the full closing of the valves in the sockets and promotes the penetration of gases into the valve cover of the engine head. For the same reason, the fuel spray in the injectors is reduced.
Negative circumstances lead to a decrease in power, fuel consumption and premature wear of the valves and fuel system units.
The dispersing properties of the Katalgen® additive are provided by the radical nature of the combustion catalysts, which contributes to the inhibition of the formation of polymer clusters and initiates the destruction of existing deposits at the molecular level.
When operating an internal combustion engine on petroleum products of various quality, a "varnish" coating is formed on the surface of the combustion chamber from unburned fuel residues and polymers, often included in the composition of octano - or cetano - boosting and depressor additives. The appearance of a temperature-resistant and oxidation-resistant polymer layer leads to the formation of carbon deposits on the valves, the walls of the pistons and cylinders, the coking of the piston rings and a decrease in the intensity of heat removal through the cylinder walls and the block head from the combustion zone. Due to overheating and reduced mobility of the piston rings, there is a violation of the cylinder geometry, which leads to a decrease in engine power, to an increase in fuel and engine oil overspending. Once the fuel enters the combustion chamber, the catalysts initiate the oxidation of the inert polymer layer, contribute to its complete burnout and release of the piston rings. De-coking of the rings increases the compression in the cylinders and returns the regular characteristics of the engine. Further operation of the internal combustion engine on fuel containing the Katalgen® additive eliminates the possibility of destructive processes of formation of deposits in the combustion chamber.
Increased catalyst life by 40%
Increased catalyst life by 40%
Prevention and cleaning of the catalytic converter
conventional fuel
fuel with Katalgen® additive


burns out in the catalytic converter
burns completely in
the engine
cylinders and initiates the oxidation
of the
previously formed carbon
deposits
Prevention and cleaning of the catalytic converter
conventional fuel

burns out in the catalytic converter
fuel with Katalgen® additive

burns completely in the engine cylinders and initiates the oxidation of the previously formed carbon deposits
More complete combustion of the fuel contributes to the reduction of carbon and its monoxide emissions. The heat generation process, which is evenly distributed throughout the entire stroke area, eliminates the possibility of zones with a critically high combustion temperature and reduces the productivity of side reactions of the formation of nitrogen oxides. The positive trend of reducing the emission of nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide and soot significantly reduces the load on the catalytic converter and increases its service life.
More complete combustion of the fuel contributes to the reduction of carbon and its monoxide emissions. The heat generation process, which is evenly distributed throughout the entire stroke area, eliminates the possibility of zones with a critically high combustion temperature and reduces the productivity of side reactions of the formation of nitrogen oxides. The positive trend of reducing the emission of nitrogen oxides, carbon monoxide and soot significantly reduces the load on the catalytic converter and increases its service life.
Reduction of engine oil consumption on carbon monoxide by 30%
Reduction of engine oil consumption on carbon monoxide by 30%
The effect of reducing the values of temperature spikes in the combustion zones increases the inertia to oxidative processes of the oil wedge, designed to lubricate the rubbing surfaces of the cylinder walls and compression rings, and to prevent the penetration of expanding gases from the combustion chamber into the engine crankcase (maintaining compression in the cylinders of the engine block).
The effect of reducing the values of temperature spikes in the combustion zones increases the inertia to oxidative processes of the oil wedge, designed to lubricate the rubbing surfaces of the cylinder walls and compression rings, and to prevent the penetration of expanding gases from the combustion chamber into the engine crankcase (maintaining compression in the cylinders of the engine block).
Increase the life of the starter and battery by 30%
Increase the life of the starter and battery by 30%
The fuel containing the Katalgen ® additive has a higher reactivity at low temperatures. This phenomenon is explained by the radical nature of the chemical compounds that make up the combustion catalysts that can reduce the level of the activity barrier of hydrocarbon molecules before and after the start of their oxidation reaction. At a higher level of the energy state, the hydrocarbon molecules are more susceptible to destruction by the oxidizer, and therefore the rate of ignition of the fuel increases dramatically. In practice, this helps to easily and quickly start the engine in normal mode, without unnecessary loads on the starter and battery.
The fuel containing the Katalgen ® additive has a higher reactivity at low temperatures. This phenomenon is explained by the radical nature of the chemical compounds that make up the combustion catalysts that can reduce the level of the activity barrier of hydrocarbon molecules before and after the start of their oxidation reaction. At a higher level of the energy state, the hydrocarbon molecules are more susceptible to destruction by the oxidizer, and therefore the rate of ignition of the fuel increases dramatically. In practice, this helps to easily and quickly start the engine in normal mode, without unnecessary loads on the starter and battery.
© 2021 KATALGEN